Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurological condition that affects an estimated 6.1 million children and adolescents in the United States alone. However, despite its prevalence, ADHD is often overlooked and misunderstood. It is often seen as a nuisance condition that only afflicts energetic little boys who are unable to sit still in class, when in reality, ADHD is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that can have severe and lasting impacts on a person's life.
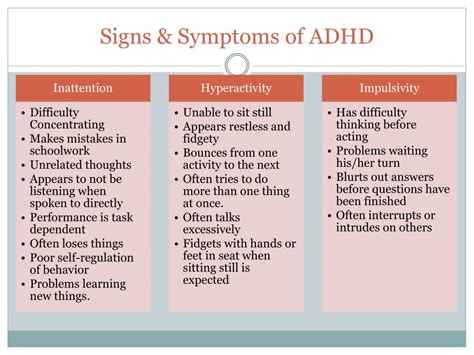
One of the biggest misconceptions surrounding ADHD is that it only affects children, but this is far from the truth. In fact, up to 60% of children with ADHD continue to experience symptoms well into adulthood. The symptoms of ADHD can vary from person to person, but generally fall into three categories: inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
People with ADHD may struggle with inattention, meaning they have difficulty focusing, staying organized, and completing tasks. They may have trouble listening to others and following through on instructions. Hyperactivity is another common symptom, which can manifest as restlessness, fidgeting, and excessive talking. Impulsivity is also a hallmark of ADHD, which can lead to impulsive decision-making, interrupting others, and difficulty waiting their turn.
While some people may dismiss these symptoms as merely annoying or frustrating, the reality is that ADHD can have serious and lasting impacts on a person's life. The symptoms of ADHD can make it difficult for people to succeed in school, work, and relationships. Studies have shown that adults with ADHD are more likely to struggle with unemployment, have lower salaries, and experience relationship problems. They may also be at higher risk for substance abuse and other mental health disorders.
The negative impact of ADHD on health is also concerning. People with ADHD have been shown to have a higher risk for obesity, cardiovascular disease, and other health problems. ADHD has also been linked to a higher risk of accidents, injuries, and risky behaviors.
Despite the serious nature of ADHD, it is often overlooked and misunderstood. One reason for this may be the fact that ADHD is often overshadowed by other neurodevelopmental disorders, such as Autism Spectrum Disorder. Another reason may be that ADHD is often seen as a "redheaded stepchild" of the neurodivergent dysfunction spectrum – a condition that is not taken as seriously as other disorders.
It is important to recognize that ADHD is a complex and serious disorder that can have significant impacts on a person's life. By understanding and acknowledging the symptoms of ADHD, we can work towards developing more effective treatments and interventions that can help people with ADHD lead successful and fulfilling lives.
References:
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Data and Statistics About ADHD. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/data.html
2. Kessler, R. C., Adler, L., Ames, M., Demler, O., Faraone, S., Hiripi, E., ... & Walters, E. E. (2005). The prevalence and effects of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder on work performance in a nationally representative sample of workers. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 47(6), 565-572.
3. Kessler, R. C., Green, J. G., Adler, L. A., Barkley, R. A., Chatterji, S., Faraone, S. V., ... & Russo, L. J. (2010). Structure and diagnosis of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: analysis of expanded symptom criteria from the Adult ADHD Clinical Diagnostic Scale. Archives of general psychiatry, 67(11), 1168-1178.
4. Mannuzza, S., Klein, R. G., Truong, N.